By Mark Wert, Catalyst Strategic Solutions Senior Advisor
Are you worried about higher interest rates and diminishing capital ratios due to accelerated, deposit-driven asset growth? Have you been adding longer-term assets, like real estate loans or agency mortgage-backed securities, to your balance sheet? Has your interest rate risk profile been increasing? If so, interest rate derivatives (IRDs) may be an effective method for managing interest rate risk (IRR).
A is for ‘application’…and casting out old assumptions
Although derivatives used to carry negative connotation because of market dynamics, the Dodd-Frank Act of 2010 increased regulation, transparency and disclosure requirements for the derivatives market, thus improving their intended use. Today, IRDs have essentially become a commoditized product that trade alongside other derivatives, such as Treasury futures, corn futures and bitcoin futures, on the Chicago Mercantile Exchange (CME).
B is for ‘benefits,’ understanding the advantages
Why should credit unions consider IRDs? Simple: They are effective, efficient tools for hedging IRR. IRDs are customizable and often the least expensive way to hedge IRR. Additionally, IRDs are easy to value, an important component when receiving hedge accounting.
C is for ‘completing the process’ or ‘connecting all the dots’
If you are concerned with your current IRR profile for any of the reasons above, let’s dive deeper. Here’s a sample scenario to demonstrate how IRDs can help manage risk.
- Identify what you want to hedge. In this example, we will use $40 million in 30-year real estate loans and call it “Mortgage Portfolio.”
- Value Mortgage Portfolio using varying prepayment speeds and rate shocks.
- Determine Mortgage Portfolio key rate durations and their values along the curve.
- Identify the risk points on the curve you want to hedge to reduce potential IRR.
- Once your risk points are determined, hedge them using pay fixed-rate/receive variable-rate swaps.
- To confirm your hedges will work, first run an analysis without the derivatives and then one with the derivatives to ensure they address IRR as expected.
As shown below, an interest rate swap is an agreement to exchange future interest payments on notional amounts at specific times, for a specified term.

By using pay fixed-rate/receive variable-rate swaps, the swaps will increase in value when rates rise, offsetting some of the market value decline in mortgages on the balance sheet. In the previous scenario, the credit union decides to hedge Mortgage Portfolio with 2-, 5- and 10-year swaps totaling $15 million in notional amount. The below chart shows how the cash flows of the Mortgage Portfolio are hedged with the swaps in three different prepayment scenarios.
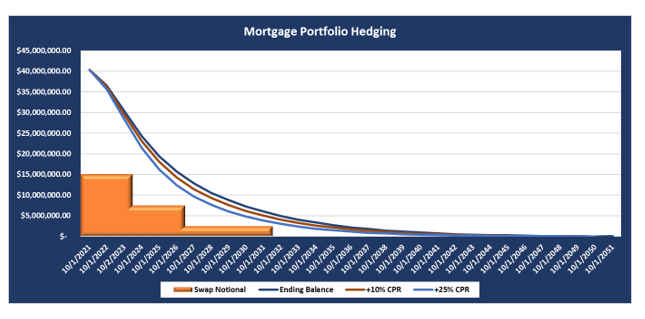
In summary, IRDs are valuable, convenient, cost-efficient tools that can be customized to suit balance sheet hedging needs. Their flexibility makes them a strategy worth considering for managing interest rate risk.
The Advisory Service experts at Catalyst Strategic Solutions have extensive experience assisting client credit unions with interest rate derivatives. Learn more about this tool as a component of your IRR management toolkit. Contact us to schedule a derivatives consultation, today.